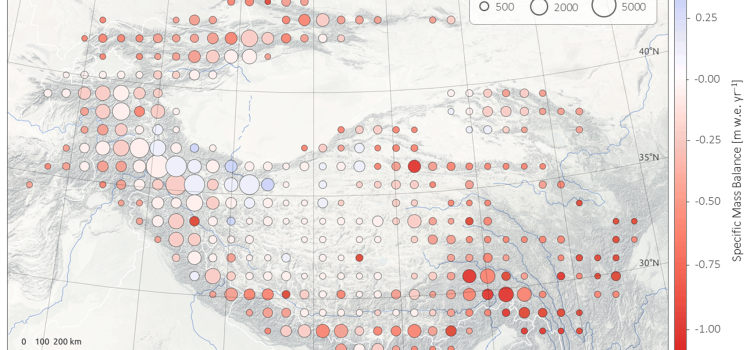
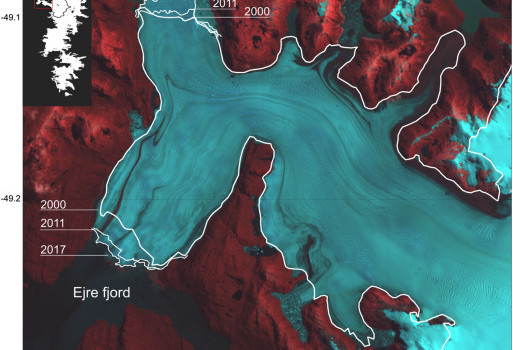
CryoSat shows that between 2010 and 2019, the Gulf of Alaska lost 76 Gt of ice per year while High Mountain Asia lost 28 Gt of ice per year. These losses are equivalent to adding 0.21 mm and 0.05 mm
CryoSat reveals ice loss from glaciers in Alaska and Asia